Overview
Given the recent oracle deviation incident of WBETH, Chaos Labs recommends updating its oracle configuration. Below, we present our analysis and recommendations.
WBETH Oracle Incident
WBETH (Wrapped Beacon ETH) is Binance’s LST that represents ETH staked into Ethereum’s PoS network. Binance runs Ethereum validator nodes on behalf of users, covering slashing risk and removing the 32 ETH minimum, so users can stake any amount of ETH. When staking, users receive WBETH at the current WBETH:ETH exchange rate, where 1 WBETH equals 1 staked ETH plus all rewards accrued since April 27 2023. WBETH does not rebase; its value grows as the exchange rate increases daily.
The WBETH–ETH exchange rate comes from exchangeRate(), a value that is manually pushed by Binance’s off-chain oracle. When users deposit ETH, the contract mints WBETH using WBETH = ETH × 1e18 / exchangeRate(). The ETH received is not staked on-chain automatically; instead, a operator later calls moveToStakingAddress() to send ETH to ethReceiver, a Binance-controlled address that handles staking off-chain. When users withdraw, their WBETH is burned and the contract converts it back to the correct ETH amount using ethAmount = WBETH × exchangeRate() / 1e18. The request is then sent to the Unwrap contract, which places it in a withdrawal queue and pays users after the lock period. If the Unwrap contract has enough ETH, it sends the calculated amount directly; if not, Binance refills the pool via rechargeAddress so withdrawals can be completed.
Currently, Venus uses a Binance oracle to price WBETH. Binance maintains a dedicated WBETH/USD Aggregator contract that stores price updates. A permitted updater calls transmit() on this contract to post the latest WBETH price with a timestamp. However, between 9:43 PM and 11:30 PM UTC on October 10, 2025, the Binance Oracle experienced a severe depeg, reporting a price far below the actual market value.
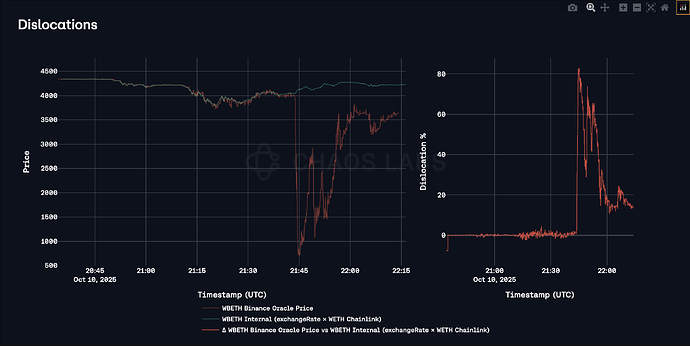
In the chart below, we compare the Binance WBETH/USD Oracle with an internal exchange-rate-based pricing method (which combines WBETH’s exchangeRate() to ETH with the ETH/USD Chainlink Oracle). As shown, the Binance Oracle deviated sharply at 9:43:50 PM UTC and dropped to a low of approximately $800, showing an 80% dislocation to its underlying value. This dislocation lasted for more than 30 minutes and only began to gradually restore its peg after 11:30 PM UTC.
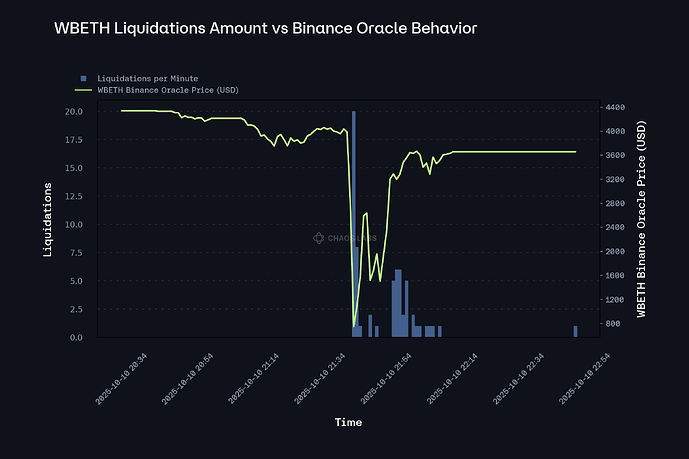
This WBETH Binance Oracle deviation directly harmed Venus borrowers. Because WBETH is used as collateral, its oracle price determines how much debt users can borrow. During the deviation, the oracle reported a WBETH price far below its true value, causing the protocol to believe users had insufficient collateral and triggering liquidations. In the end, this resulted in a total of 65 unnecessary liquidations (WBETH as the seized collateral).
WBETH Oracle Recommendation
To prevent similar incidents in the future, we recommend updating the WBETH pricing configuration to leverage the exchangeRate() function from the WBETH contract to determine the on-chain WBETH-to-ETH conversion, and then apply Venus’s Resilient Oracle to price ETH. This approach ensures that WBETH’s value consistently reflects its underlying ETH plus accrued rewards, rather than relying on an external price feed that may diverge from intrinsic value.
In addition, following the deviation incident, Binance revised how it prices WBETH on its own platform, moving away from a market-based price source and adopting an exchange-rate-based model that derives WBETH’s value from its staking conversion rate, in order to prevent similar pricing dislocations. However, the on-chain Binance Oracle currently used by Venus is still manually updated via transmit() and does not guarantee alignment with Binance’s new internal pricing logic, which means it may reproduce the same risk. This further strengthens the case for Venus to explicitly migrate to an exchange-rate-driven oracle design instead of relying on the legacy Binance Oracle.
CAPO
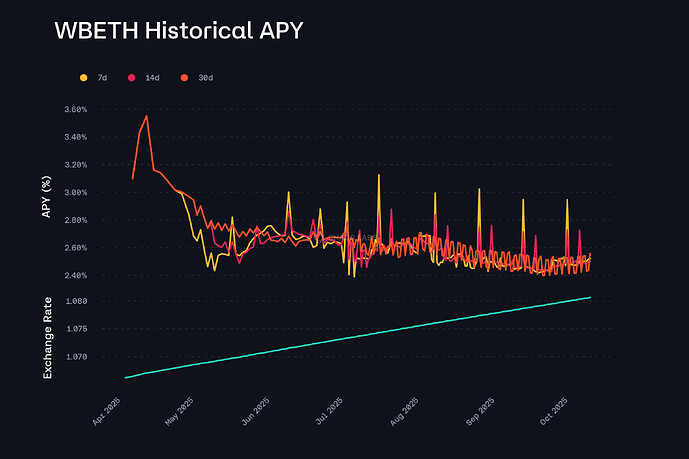
We also recommend using a CAPO oracle to better manage WBETH overpricing risk. To evaluate rate behavior, a 14-day average is applied to the yield series to smooth daily changes. Based on the most recent 180-day window, the maximum 14-day annualized APY observed is 3.14%, and the standard deviation of the 1-day APY series is 1.50%. These values are added to produce an Annual Growth Rate of 4.64% for the Capped Oracle.
A 30-day snapshot interval is applied to ensure consistent monthly updates of the reference exchange rate. To avoid prematurely capping legitimate growth immediately after deployment, we apply a snapshot gap equivalent to one month of yield at the selected annual growth rate; this results in a gap of 0.39%
Specification
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual Growth Rate | 4.64% |
| Snapshot Interval | 30d |
| Snapshot Gap | 0.39% |
Disclaimer
Chaos Labs has not been compensated by any third party for publishing this recommendation.